HTTP or hypertext transfer protocol is a key protocol for exchanging data on the web. It was made to create the first interactive text based web browser or the original world wide web. It is an application layer TCP/IP based protocol used to deliver data (HTML files, images, etc.). HTTP operates on port 80 by default and it is a stateless protocol.
We all know there are numerous security issues with HTTP from cross site scripting to HTTP request smuggling, which is why HTTP connection is combined with SSL or TLS and they call it HTTPS which uses port 443 by default.
HTTP over SSL was created to allow sending HTTP messages over an SSL secured channel, but today, TLS is utilized, since it is the successor of SSL. SSL and TLS are both cryptographic protocols and they only have minor differences. For example, in SSL, hash calculation comprises the master secret and pad while in TLS hashes are calculated over handshake messages. Also, SSL message authentication adjoins the key details and application data in an ad-hoc way while TLS relies on hash based message authentication code. All in all, TLS is just an upgraded version of SSL.
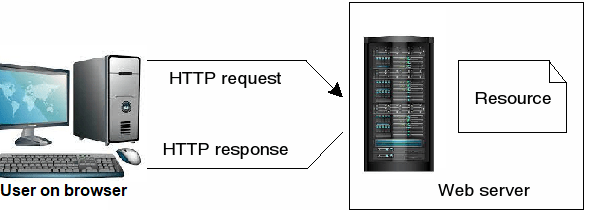
HTTP as laid out in RFC 2068 defines what actions can be requested by clients and how servers should answer those requests. Usually the clients will send requests through port 80 for HTTP or 443 if using HTTPS to HTTP server to download things like text or graphics. These files are then returned to the client and the connection closes afterwards.
You must be logged in to post a comment.