Syslog or system logging is a standard protocol that is used to send system log or event messages to a central location, usually the log server that stores the log files. The protocol simply allows the systems to write messages to log files using syslog. Log used for management purposes to include analysis, performing audits, troubleshooting, and other tasks. The default port it uses is 514.
The log messages include things like timestamp, severity rating, device ID to include IP address, and information that defines an event. In a syslog message, header has a priority level, which is a combination of a code for the process of the device creating the message and the severity level. Severity levels usually range from 0 for emergencies to 7 for debug messages.
The log server with the log files makes it easy to monitor multiple devices like switches, firewalls, and servers. The syslog can categorize and provide a comprehensive view of your network and trace outages. Usually there is management and filtering software that enables the server to generate alarms and alerts automatically. Security information and event management software provides a way to track the vast amount of log data that syslog collects. This way, sysadmins are quickly alerted of any issues.
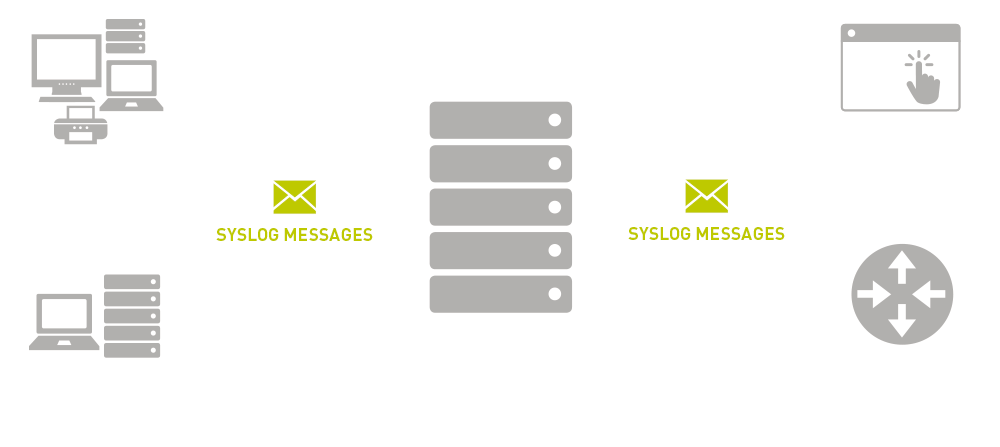
The biggest downside regarding syslog is that it is a connectionless protocol. The messages are sent via user datagram protocol, so messages aren’t acknowledged or guaranteed to arrive. However, both syslog-ng and rsyslog can also use TCP, TLS, and RELP, in addition to UDP.
Many confuses syslog with SNMP trap, but while they may be similar, there are differences. SNMP is generally used for network monitoring while syslog is multi-purpose. SNMP is great for constrained situations with predictable conditions while syslog is wider in scale and less constrained, and covers wider range of events.
You must be logged in to post a comment.