Screened subnet or DMZ was developed to protect the organization’s trusted local area network from untrusted traffic. This architecture uses a firewall or firewalls to separate a network into three different zones.
First, we have the internet, the untrusted zone. The untrusted zone communicates with a lot of business servers like domain name systems or email servers, so the firewall has to be configured to let the external traffic in. Then we have the local area network or organization’s private network that we want to protect in the trusted zone.

If these trusted zone is behind a single firewall along with the external facing servers that communicate with the internet a lot, then the attackers can simply pivot from the external facing servers and attack the trusted zone systems. Basically, attackers already made it through the firewall. This is why an extra zone is created as a buffer called screened subnet or DMZ. External facing servers like domain name system or email are placed there. The firewall policies will be different for screened subnets or DMZ compared to trusted zones. You can use a single firewall to separate the three zones, but it’s recommended to have two firewalls and have DMZ or screened subnet in between the trusted and untrusted zones.
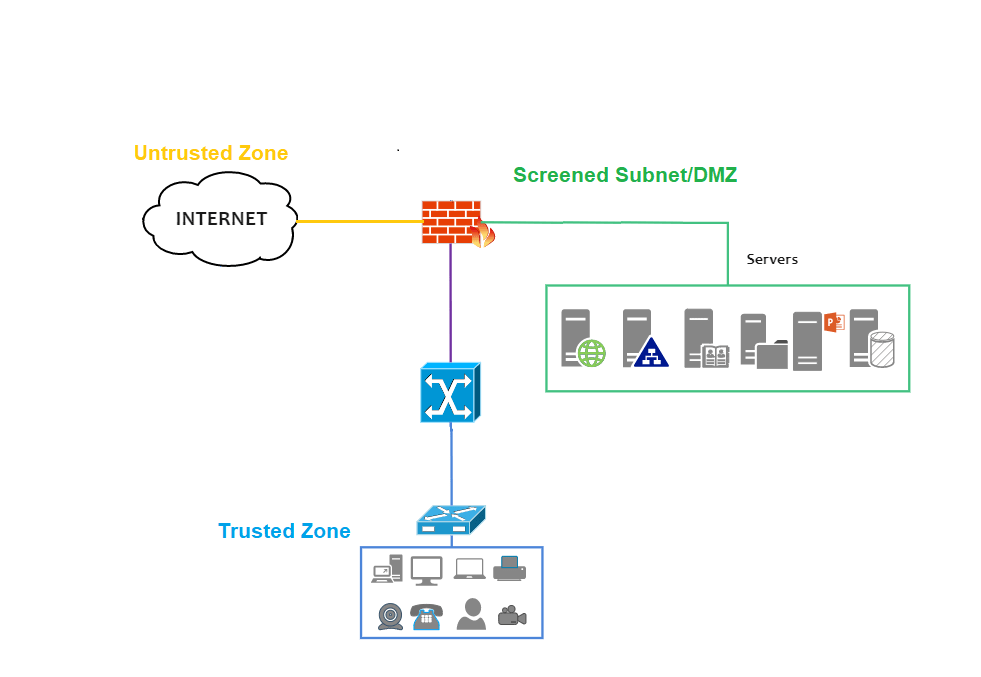

In zone based Firewalls, device interfaces are placed in trusted, untrusted or screened subnet zones and policies are applied to these zones. One of the advantages of applying policies on zones rather than interfaces is that whenever new changes are required at the interface level, policies are applied automatically simply by removing or adding to an interface in a particular zone.
You must be logged in to post a comment.