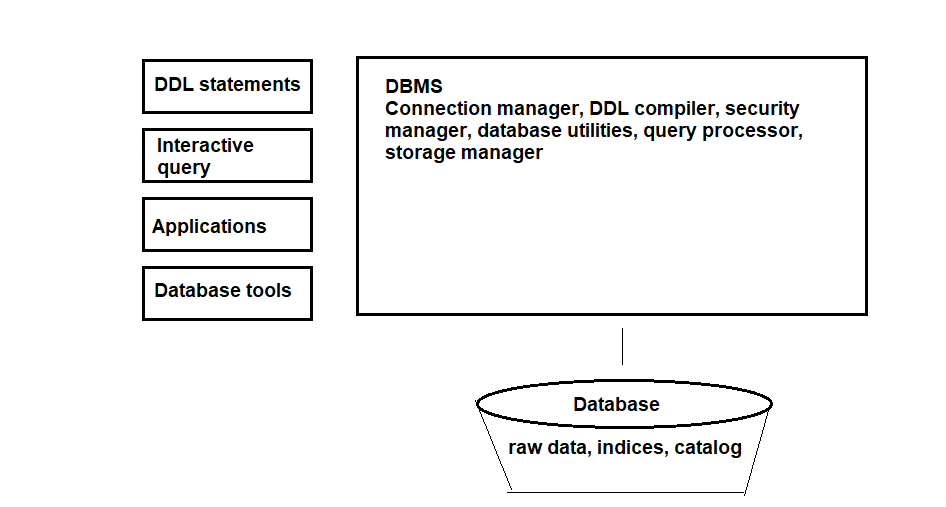
Let’s go over key components that make up a database management system. As you can see on the image below, we have methods of interacting with the DBMS and the DBMS itself on the right. DBMS itself is connected to a database with raw data, indices, and catalog. DDL statements, interactive query, applications, and database tools are methods of interacting with DBMS, which means the components within DBMS should be able to respond to the interactions and provide the appropriate interfaces.
DDL or data definition language simply allows one to create/modify structure of objects in a database. Objects are anything that stores data or references, like tables, indices, and users. DDL statements can be things like drop, create, alter tables and can be executed using a command line interface. DDL statements are handled by DDL compiler portion of DBMS, where it parses the DDL, checks for errors, translates and registers the data in the catalog portion of the database it is connected to.
Then we have the interactive query that can be accessed by command line or graphical user interface that provides the capability to execute DML or data markup language. While DDL focuses on creating and modifying database objects like tables, DML is focused on manipulating the data within the database. Applications are able to use embedded DML statements to interact with DBMS. Just like DDL compiler, we have DML compiler that accomplishes similar tasks. DML compiler works closely with query processor as well, which includes query parser/rewriter, query optimizer, and query executor.
Lastly, we have database tools for interaction side, which includes various tools that are used to maintain and fine tune DBMS.
Now let’s take a look at the DBMS side of things and how it provides the appropriate interfaces to ensure tasks that are requested are executed appropriately. First, we have the connection and the security manager. Connection manager is what verifies logon credentials and returns a connection handle. Security manager on the other hand handles what privileges a user may have, like read or write rights and to what particular sets of data.
Next we have the DDL compiler, which we talked about. It registers data definitions within the catalog in the database. Catalog is utilized by other parts of the DBMS. Then we have the query processor that deals with the data portion of it. DML compiler extracts DML statements from host language and works with other components to execute the DML statements. We have query parser that parses query into internal representation format and is checked for errors. The query rewriter then optimizes the query and simplifies it that are DBMS specific. The query optimizer then comes up with query execution plans and finds out the most cost effective way by aggregating estimated CPU processing cost, time, and other factors. Then the query executor calls on the storage manager to retrieve the data.
Storage manager manages accesses to the file and storage of the data. It encompasses buffer manager, lock manager, transaction manager, and recovery manager. Transaction simply oversees task executions like read/write operations, buffer is responsible for caching, lock manager is responsible for concurrency control, and recovery keeps track of all its operations on logfile and ensures rollback.
DBMS utilities outside of this exists like loading utility to support mass transfers, monitoring utilities for reports, and so on.
You must be logged in to post a comment.